Proxing Google Tag Manager
This guidance is for publishers and tag implementers who have access to Cloudflare DNS and Worker Services. There is likely to be some small additional cost to running the proxy. You can explore those costs by visiting this link.
Do note that this guidance is for general information only and is not a requirement for running the Anonymised Marketing tag. Anonymised is not an agent nor an affiliate of Cloudflare.
Why Proxy Google Tag Manager (GTM)
There are 3 main reasons for exploring running GTM through a proxy:
Speed. Using the Cloudflare CDN can have considerable performance benefits for sites running GTM.
Security. Hosting a subdomain to proxy GTM makes it less prone to cross-site scripting attacks.
Reliability. Google Tag Manager is prone to Adblockers and other privacy initiatives stopping the service and the scripts that it manages from executing.
How to configure Cloudflare to serve as the GTM proxy
Go to your Cloudflare account and set up a new worker.
Write a script to respond to another site and use a cache API. In the example below, we receive the call to the proxy URL, check the cache and respond appropriately:
CODE// Make sure you update this following line for your GTM container URL and ID const GTM_URL = 'https://www.googletagmanager.com/gtm.js?id={GTM CONTAINER ID}'; const CACHE_EXPIRY = 30; // cache timeout in seconds // Listen to any incoming requests and apply our function addEventListener('fetch', function(event) { try { event.respondWith(handleRequest(event)) } catch(e) { console.error(e) } }) async function handleRequest(event) { const request = event.request // Only GET requests work with this proxy. if (request.method !== 'GET') return MethodNotAllowed(request) // https://developers.cloudflare.com/workers/examples/cache-api const cacheURL = new URL(request.url); const cacheKey = new Request(cacheURL.toString(), request); const cache = caches.default let response = await cache.match(cacheKey); if (!response) { // If not in cache, get it from origin response = await fetch(GTM_URL); // Must use Response constructor to inherit all of response's fields response = new Response(response.body, response) response.headers.append("Cache-Control", `s-maxage=${CACHE_EXPIRY}`) // Store the fetched response as cacheKey // Use waitUntil so you can return the response without blocking on // writing to cache event.waitUntil(cache.put(cacheKey, response.clone())) } return response } // Use the following when the request is not a valid GET request function MethodNotAllowed(request) { return new Response(`Method ${request.method} not allowed.`, { status: 405, headers: { 'Allow': 'GET' } }) }
Note: This is example code only, please conduct your checks before deploying and be sure to check the cache timeout to your preference.
Set up a subdomain to host the worker using Cloudflare DNS:
In your Cloudflare zone file, create an entry similar to the following:
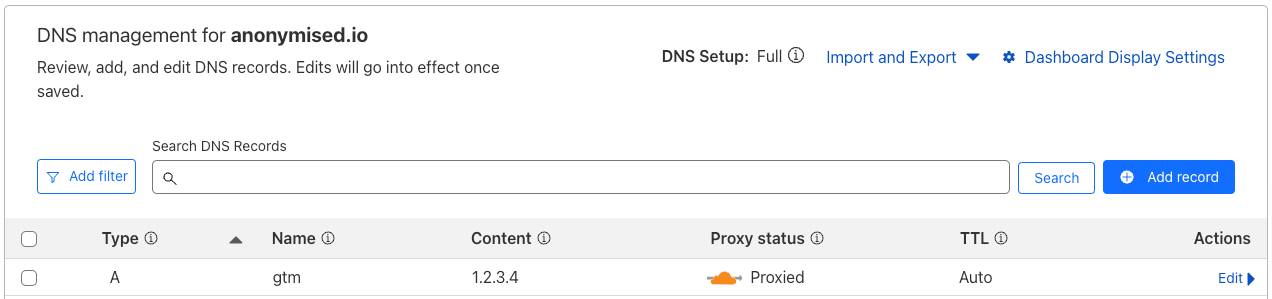
Example of the required DNS entry
Note that the Cloudflare Worker will intercept the request before it reaches any IP address, so you may use a dummy IP address to enable the saving of the DNS entry.
Map the Worker to the subdomain by navigating to the Workers Routes, in your Cloudflare dashboard, and adding a new route, similar to the following:
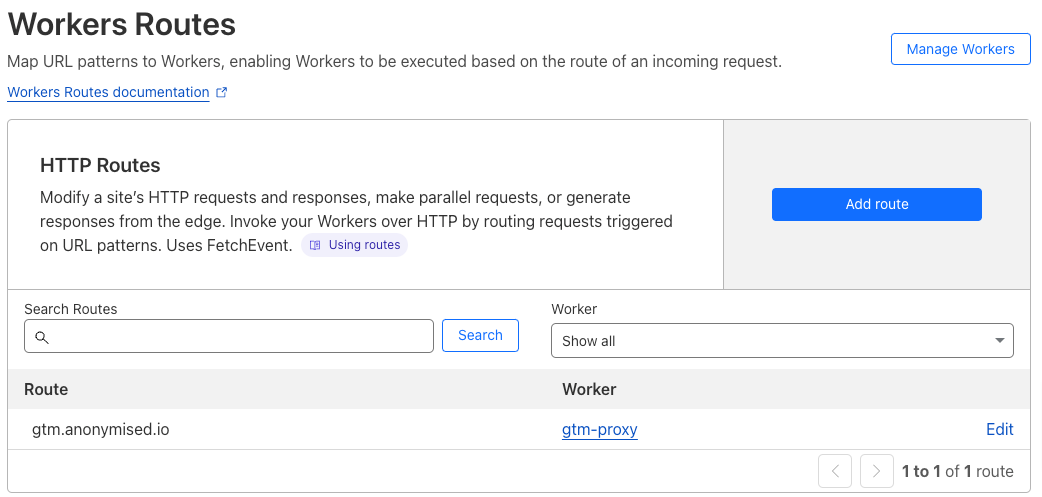
Mapping the Worker to the subdomain
Finally, alter the GTM snippet on your site to reference the proxy URL with that of Googles. This means replacing the line of script googletagmanager.com with your subdomain as created above. See example below:
CODE<!-- Google Tag Manager --> <script>(function(w,d,s,l,i){w[l]=w[l]||[];w[l].push({'gtm.start': new Date().getTime(),event:'gtm.js'});var f=d.getElementsByTagName(s)[0], j=d.createElement(s),dl=l!='dataLayer'?'&l='+l:'';j.async=true;j.src= 'https://gtm.your-domain.com';f.parentNode.insertBefore(j,f); })(window,document,'script','dataLayer','GTM-XXXXX');</script> <!-- End Google Tag Manager -->
Note that in the example we have also removed the Container ID, as this is not necessary on the page, and is set in the Worker Script, thus improving site security.
As with all customisation, we strongly suggest that adequate testing is performed before making such critical changes and where possible a sandbox environment should be used.
